The human body is an incredible machine with various systems at work, and one of the most vital systems is the urinary tract. The urinary tract comprises the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, and it plays a pivotal role in removing waste and maintaining the body's fluid balance. As we're delving deeper into the anatomy and histology of the urinary tract, let us explore the wonders of this unique system that keeps us healthy and well. The kidneys, situated in the abdominal cavity, are bean-shaped organs whose primary function is to filter the blood and remove toxins, excess water, and electrolytes from the body. The kidneys' inner structure has nephrons, tiny units that filter the blood and produce urine, which travels through the ureters to the bladder. This process is crucial in maintaining a healthy fluid balance in the body. The ureters are slender tubes, whose primary function is to transfer urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The bladder, situated in the lower abdomen, is a hollow muscular organ that stores urine until it's full. A healthy bladder can store up to 1.5 to 2 cups of urine comfortably. As the bladder fills up, it signals the brain to initiate the urge to urinate. In contrast, the urethra is a tube that connects the bladder to the external opening, and it's responsible for the elimination of urine from the body. Maintaining a healthy urinary tract is vital in preventing urinary tract infections, kidney stones, bladder cancer, and other urinary tract disorders. The pediatric population is also susceptible to a wide range of urinary tract disorders. Nephrolithiasis, commonly known as kidney stones, is a relatively common issue that affects children. It is essential to identify the underlying causes and appropriate treatment measures to manage any urinary tract disorders effectively. In conclusion, the urinary tract is a vital system that performs a wide range of functions in maintaining your overall health. The kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra work together seamlessly to eliminate waste and maintain a healthy fluid balance in the body. It's essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle, stay hydrated, and seek medical attention if you experience any urinary tract issues. Stay healthy and take care of your precious urinary tract!
If you are looking for Multi-modality imaging review of congenital abnormalities of kidney and you've came to the right place. We have 6 Images about Multi-modality imaging review of congenital abnormalities of kidney and like Pediatrics | 9.2 Pediatric urinary tract : Case 9.2.7 Nephrolithiasis, Ureteral Stents, Nephrostomy Tubes, and Urethral Dilators | Abdominal Key and also Multi-modality imaging review of congenital abnormalities of kidney and. Here it is:
Multi-modality Imaging Review Of Congenital Abnormalities Of Kidney And
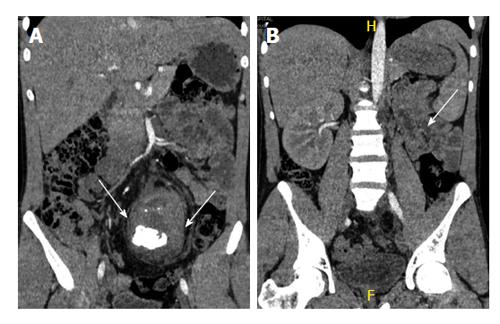 www.wjgnet.com
www.wjgnet.com kidney abdominal coronal figure ectopic calculus pelvis recurrent tomography computed contrast pain lower standing non man long year old
Ureteral Stents, Nephrostomy Tubes, And Urethral Dilators | Abdominal Key
 abdominalkey.com
abdominalkey.com ureteral nephrostomy urethral tubes stents obstruction renal urinary lower upper tract surgery dilators fig sites key open
Pediatrics | 9.2 Pediatric Urinary Tract : Case 9.2.7 Nephrolithiasis
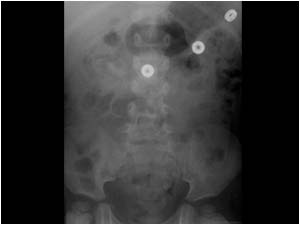 www.ultrasoundcases.info
www.ultrasoundcases.info nephrolithiasis ultrasoundcases
Management Of Urinary Calculus
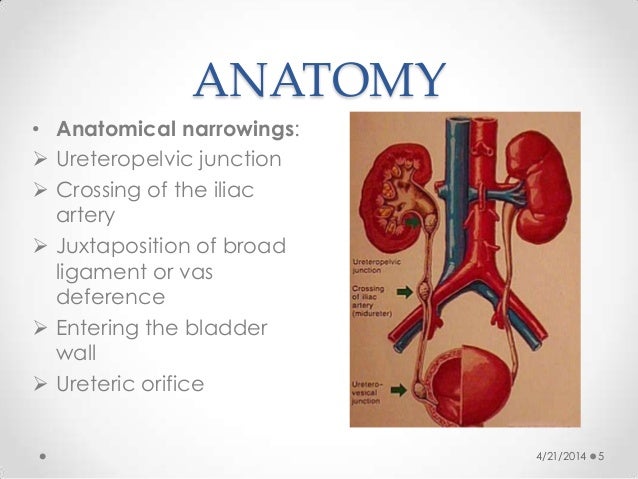 www.slideshare.net
www.slideshare.net urinary calculus ureteropelvic
Anatomy & Histology Of The Urinary Tract - Medatrio
 medatrio.com
medatrio.com anatomy urinary pole upper lower lateral convex anterior surface kidney margin medial tract histology posterior concave thicker conical thick flat
Pediatrics | 9.2 Pediatric Urinary Tract : Case 9.2.7 Nephrolithiasis
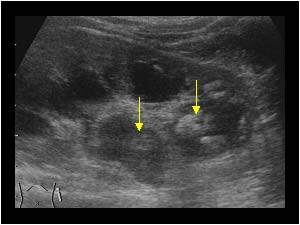 www.ultrasoundcases.info
www.ultrasoundcases.info nephrolithiasis calculi pelvis dilatated echogenicity renal urinary tract
Multi-modality imaging review of congenital abnormalities of kidney and. Anatomy urinary pole upper lower lateral convex anterior surface kidney margin medial tract histology posterior concave thicker conical thick flat. Nephrolithiasis calculi pelvis dilatated echogenicity renal urinary tract
 www.wjgnet.com
www.wjgnet.com  abdominalkey.com
abdominalkey.com  www.ultrasoundcases.info
www.ultrasoundcases.info  www.slideshare.net
www.slideshare.net  medatrio.com
medatrio.com  www.ultrasoundcases.info
www.ultrasoundcases.info
Keine Kommentare:
Kommentar veröffentlichen